
photo: Wild Rose Images
California Senator Dianne Feinstein’s move to put a large swath of the Mojave Desert off-limits to renewable energy development is splitting the environmental movement and could derail some two dozen solar and wind power projects the state needs to comply with its ambitious climate change laws.
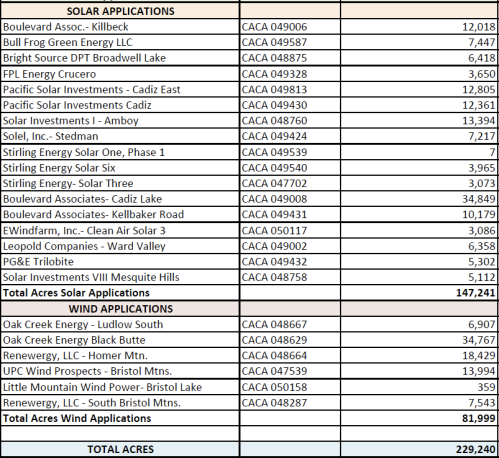
On the firing line are 17 massive solar power plants and six wind farms planned for federal land — land that would be designated a national monument under legislation Feinstein intends to introduce. The solar projects in question would be built by a range of companies, from startups BrightSource Energy and Stirling Energy Systems to corporate heavyweights Goldman Sachs (GS) and FPL (FPL), according to federal documents. (For the complete list, see below.)
The companies are among scores that have filed lease claims on a million acres of acres of desert dirt controlled by the U.S. Bureau of Land Management. California utilities PG&E (PCG) and Southern California Edison (EIX) have signed long-term power purchase agreements for some of the projects now in jeopardy and are counting on the electricity they would produce to meet state-mandated renewable energy targets. PG&E itself has filed a solar power plant land claim in the proposed national monument.
The area of the desert in dispute is some 600,000 acres formerly owned by Catellus, the real estate arm of the Union Pacific Railroad, and donated to the federal government a decade ago by the Wildlands Conservancy, a Southern California environmental group. About 210,000 of those acres are managed by the U.S. Bureau of Land Management, which opened part of the land to renewable energy projects.
“Many of the sites now being considered for leases are completely inappropriate and will lead to the wholesale destruction of some of the most pristine areas in the desert,” Feinstein wrote in a letter to Interior Secretary Ken Salazar released last week, notifying him that she will introduce legislation to designate the former Catellus lands a national monument. “Beyond protecting national parks and wilderness from development, the conservation of these lands has helped to ensure the sustainability of the entire desert ecosystem by preserving the vital wildlife corridors.”
The Catellus land controlled by the BLM forms something of a golden triangle between the Joshua Tree National Park and the Mojave National Preserve in Southern California and are particularly coveted for renewable energy development because of its proximity to transmission lines.
Alan Stein, a deputy district manager for the BLM in California, told Green Wombat that the solar and wind lease claims are in areas that are not designated as wilderness or critical habitat for protected species like the desert tortoise. “This is public domain land, ” he says.
Tortoises, however, are found across the Mojave, and battles over Big Solar’s impact on endangered wildlife are quietly brewing in several solar power plant licensing cases now being reviewed by the California Energy Commission. Environmentalists find themselves walking a thin green line, trying to balance their interest in promoting carbon-free energy with protecting fragile desert landscapes and a host of threatened animals and plants.
Take BrightSource Energy’s Ivanpah 400-megawatt solar power plant complex on the California-Nevada border. The three solar power plants to be built by the Oakland-based company will supply electricity to PG&E and Southern California Edison. But the project will also destroy some 4,000 acres of desert tortoise habitat and at least 25 tortoises will have to be relocated – a somewhat risky proposition as previous efforts in other cases have resulted in the deaths of the animals.
On Wednesday, the California Energy Commission granted two national environmental groups – the Defenders of Wildlife and the Sierra Club – the right to intervene in the Ivanpah case. “Defenders strongly supports … the development of renewable energy in California,” Kim Delfino, California program director for Defenders of Wildlife, wrote to the energy commission in a Jan. 23 letter. “Defenders has several serious concerns about the potential impacts of this project on a number of rare, declining and listed species and on their associated desert habitat and waters.”
Natural Resources Defense Council attorney Johanna Wald wrote a letter with the Wilderness Society expressing concern over the impact of Ivanpah project on the desert tortoise but also made a strong statement of support for renewable energy development. “Our public lands harbor substantial wind, solar, and geothermal resources,” wrote Wald, who serves on a state task force to identify appropriate areas for renewable energy development. “Developing some of these resources will be important to creating a sustainable energy economy and combating climate change.”
The big national enviro groups are working with the government and power plant developers to create zones in the Mojave where renewable energy projects would be permitted while setting aside other areas that are prime habitat and wildlife corridors. A similar effort is underway on the federal level to analyze the desert-wide impact of renewable energy development.
Local environmental organizations, however, have split with the Big Green groups over developing the desert and other rural areas. In San Luis Obispo County, Ausra, SunPower (SPWRA) and First Solar’s (FSLR) plans to build three huge solar farms within miles of each other has prompted some local residents worried about the impact on wildlife to organize in opposition to the projects.
And some small Mojave Desert green groups pledge to go to court to stop big solar projects. “We don’t want to see the Endangered Species Act gutted for the sake of mega solar projects,” veteran grass roots activist Phil Klasky told Green Wombat last year for a story on the solar land rush in the Mojave. “I can say the smaller environmental organizations I’m involved with are planning to challenge these projects.”
It would be unwise to underestimate Klasky. In the 1990s, he helped lead a long-running and successful campaign to scuttle the construction of a low-level radioactive waste dump in tortoise territory in the Mojave’s Ward Valley – now a prime solar spot.
Still, while California’s senior senator’s move in the Mojave may exacerbate rifts in the environmental movement over renewable energy, it also could galvanize efforts to resolve critter conflicts in a comprehensive way. Otherwise, environmentalists of varying hues may find themselves fighting each other rather than global warming.
Update: I just had a conversation with BrightSource spokesman Keely Wachs, who takes issue with my characterization that the Ivanpah project will “destroy” desert tortoise habitat. He points out that the company is taking care to minimize the impact of the power plant on the surrounding desert and that wildlife may still occupy the site. It would be more accurate to say that the project will remove desert tortoise habitat from active use during Ivanpah’s construction and operation.
(Below is a list of solar and wind projects that fall within the proposed Mojave national monument. Note: Solar Investments is a subsidiary of Goldman Sachs and Boulevard Associates is a subsidiary of FPL.)
source: BLM
Read Full Post »




 Here’s an iPhone app that really could help save the planet while saving stressed consumers’ money: Boulder, Colo.-based startup Tendril this week unveiled a mobile software program that lets people monitor and control their home’s energy use while on the go.
Here’s an iPhone app that really could help save the planet while saving stressed consumers’ money: Boulder, Colo.-based startup Tendril this week unveiled a mobile software program that lets people monitor and control their home’s energy use while on the go. Another reason Green Wombat will be spending Earth Day in Southern California this year: Former President Bill Clinton will deliver the keynote speech at Fortune Magazine’s
Another reason Green Wombat will be spending Earth Day in Southern California this year: Former President Bill Clinton will deliver the keynote speech at Fortune Magazine’s 


